When teams can’t agree on which Salesforce data is important, keeping everything seems like the safest choice. But in reality, this can lead to compliance risks and storage problems. A Salesforce data retention policy defines how long different types of data are stored, archived, or deleted in your org. This helps teams make consistent decisions, protect customer information, and keep orgs running smoothly.
Data retention is the practice of storing data for a defined period of time to meet business, legal, or compliance requirements. Careful data storage is a crucial part of the data lifecycle and should be a consideration at each stage, from creation and use to ongoing maintenance, storage and updates, and eventual archiving or deletion. A strong Salesforce data retention policy can help you maintain system health and protect your data from both accidental loss and security threats.
But where do you start? From understanding regulatory requirements to automating data management processes, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to build a robust retention strategy that works for your org.
How do retention policies work?
Instead of keeping all of your data forever, it’s best practice to set a retention policy that defines how data is managed throughout its lifecycle.
You can set automated rules in Salesforce to archive data after a set period of time, ensuring consistent data management without manual intervention. This helps keep you compliant while supporting your org to run smoother and faster.
Salesforce retention policies cover the full data lifecycle, from creation and storage to archiving and deletion. Each stage carries its own set of rules and timelines that you can customize based on your business needs.
How long is data kept in Salesforce?
Salesforce doesn’t have a single default retention period, instead different products and data types each have their own. Knowing these defaults can help you plan your data management strategy. Here’s what you need to know about these retention timelines:
- Recycle Bin: Salesforce keeps data in the Recycle Bin for 15 days by default, giving you a brief window to recover accidentally deleted records (this can be extended to 30 days in Salesforce Classic).
- Field History: Field history data is retained for 18 months in the org and 24 months via API, allowing you to track changes over time.
- Marketing Cloud: Marketing Cloud engagement data is retained for 730 days as of June 2025 — keep this in mind when planning your marketing campaigns.
- Data Cloud: In Data Cloud, retention is set with lifecycle policies on Data Lake Objects (DLOs). There’s no UI yet for retention limits, so you’ll need to raise a Salesforce support case with the DLO’s developer name and the retention period (in days).
User-created Marketing Cloud data extensions have no retention limit unless configured, which means they’ll stay in your org indefinitely until you take action. This flexibility lets you decide what’s worth keeping long-term, but it also means you need to be proactive about setting appropriate limits to avoid unnecessary storage costs.
Standardizing Salesforce delivery in Manufacturing: Lessons from a release team
On-platform and off-platform data retention
Whether data is archived or backed up, you need a clear plan for how long to keep it and where. Knowing the difference between archiving and backup, and how each can be managed on and off the Salesforce platform, helps you make the right choices for your data.
Archiving in Salesforce moves older data that you don’t need every day out of your org, while keeping it accessible for reporting and compliance. You can still search for and view archived data through specialized interfaces or widgets within Salesforce when you need them. This ensures business continuity while reducing clutter in your active org. You can do this on-platform with Big Objects, or off-platform with an external archive that stays accessible when needed.
Off-platform archiving stores data externally but keeps it accessible when you need it, giving you flexible data retention without using up your org’s storage. Solutions that offer off-platform archiving, like Gearset, give you more control over retention periods, storage and access. Third-party tools often outperform native Salesforce solutions in data retention, offering automated policies, detailed object-level rules, and built-in backup with archiving.
Backups store copies of your data and metadata so you can restore if needed. Salesforce offers the Salesforce Backup managed package as a native solution, but many teams choose third-party solutions for more granular control, faster recovery, and combined backup and archiving in one place. Storing backups off-platform also adds an extra level of security by isolating your backups from potential issues or vulnerabilities within the Salesforce platform itself.
Whether you’re archiving or backing up, retention policies help you stay in control — deciding how long data is kept, when it should be deleted, and how to meet compliance without overloading your org.
Why you shouldn’t store everything in Salesforce
Data retention is about making smart decisions to keep your system running smoothly, your costs under control, and your customer data protected. Here’s why this matters in a Salesforce context.
Compliance and regulations
Most Salesforce orgs hold data that falls under strict regulatory requirements like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations define not only how you collect and store data but also when you need to delete it. Retaining data beyond its required period can put your business at risk of non-compliance, leading to fines or legal complications. A strong data retention policy helps you maintain data privacy by ensuring that sensitive records are stored securely and deleted when no longer needed.
The 7-year retention rule is a common standard for financial and business records. A requirement of SOX, this rule means certain records – like transactions, contracts, and audit trails — need to be kept for at least seven years in Salesforce. Knowing if this rule applies to your data helps you keep what’s needed without holding onto too much.
Storage limits and costs
Salesforce doesn’t offer unlimited storage, and exceeding your limits comes with added costs. Every record, file, and attachment takes up space, and as your org grows, storage can quickly become an expensive problem. If you don’t actively manage your data retention, you’ll find yourself paying for additional storage or scrambling to free up space at the last minute.
System performance
The more data you keep in your Salesforce org, the harder your system has to work. Large datasets can slow down searches and processing times for reports, frustrating users and reducing productivity. This can delay your customer support response times or lead to decisions made based on outdated reports.
Agents and AI also thrive on clean, current data. Legacy records and stale datasets don’t just slow down your org, but also the accuracy and usefulness of Agentforce. A retention policy helps your org stay fast, focused, and future-ready.
Security and risk management
The more data you store in Salesforce, the greater the risk of exposure — especially as users, permissions, and integrations increase too. Sensitive data, like customer information and financial details, become a liability if kept longer than necessary. Unused or outdated data increases your attack surface, making breaches more damaging and compliance harder to manage.
Off-platform archiving and backups ensure data is still accessible during a Salesforce outage, while giving you the control to enforce retention policies without bloating your org. This means your data is always recoverable.
Best practices for implementing a data retention policy in Salesforce
A robust Salesforce data retention policy helps you stay compliant, optimize storage, and protect sensitive information. But before putting one in place, there are a few key factors to consider.
Identify your compliance requirements
Retention policies are often needed to make sure your company’s archiving and backup practices comply with relevant data protection legislation like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These govern how long certain types of data must be retained and when they should be deleted. Work with your legal and compliance teams to ensure your policy aligns with these rules. Consider records like Cases, Opportunities, and field history tracking, which may have specific legal or operational retention requirements.
To stay GDPR compliant, your retention policy needs to cover data subject requests, including the right to be forgotten. Retain a clear record of why you’re keeping data, and set up automated deletion when retention periods end. Regularly review your process so you’re ready for regulator reviews.
Categorize data to align with business objectives
Not all data is equally important. Some records, like customer transactions or audit logs, may need to be kept for legal reasons, while others, such as old email logs, may have no long-term value. Categorizing data helps define what to archive, delete, or store long-term.
Implement access controls
Data retention governs both how long information is kept and who is allowed to access it. Enforcing role-based access controls (RBAC) ensures that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive records, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or accidental deletion.
Anonymize and strip out personal data
Handle personal data with care. Personally identifiable information (PII) needs clear rules in your retention policy. Salesforce gives you a few ways to anonymize it:
- Privacy Center can auto-clear PII fields once data hits its expiry.
- Field-level encryption lets you lock sensitive info, then wipe it for good by deleting the keys.
- Custom Apex can swap out PII with fake values while keeping record links intact for reporting.
Just make sure you’re removing all details that could identify someone — even innocent-looking ones that, combined, could point to a real person.
Document and review your retention process
A well-documented retention policy provides clear guidelines on what data to keep, for how long, and how deletions or archives are handled. This helps ensure consistency, makes compliance audits easier, and allows teams to follow best practices without confusion.
Regularly review your data retention policy
Business needs, regulations, and storage constraints change over time. Set a schedule to review and update your policy to ensure it stays relevant and your data lifecycle management continues to meet compliance and operational requirements. Storage costs can also play a role and while Gearset doesn’t charge based on data volume, some providers do, so reviewing and adjusting retention periods can help avoid extra costs.
Plan for data restoration
While archiving helps manage storage by moving older records out of your live org, it doesn’t protect against accidental deletions or corruption. Confident releases start with reliable backups. Retention policies help you decide what to keep, but a strong backup strategy ensures you can roll back changes and restore what matters if something goes wrong. Together, they give your team the confidence to move fast without risk.
Automate data deletion and archiving
Manually managing retention can be time-consuming and error-prone, disrupting critical business processes and increasing the risk of data loss. Automating data deletion and archiving, either through scheduled jobs in Salesforce, third-party tools, or custom Apex scripts, ensures records are removed or archived consistently.
Carry out user training and enforce data governance
A retention policy is only effective if people follow it. Enforcing governance policies and training your team in data handling best practices will prevent unnecessary data accumulation and security risks.
How to implement a data retention policy using native tools on Salesforce
Once you’ve defined your data retention policy, and decided what to keep, archive, or delete, it’s possible to configure your Salesforce instance to put it into action — although the native tools have their limitations.
1. Automate deletion with Privacy Center: Privacy Center is a paid add-on that supports compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA. It lets you create policies that automatically delete or anonymize personal data based on retention rules.
2. Use Big Objects for historical data retention: Salesforce offers Big Objects as a native solution. Big Objects store high-volume data without affecting standard storage limits. This can help you retain high-volume data like logs, transactions, or audit trails while keeping your active org running efficiently.
As Big Objects don’t have a standard UI you can’t browse them like regular Salesforce records. Accessing data requires SOQL queries, which makes them less user-friendly than standard objects. There’s also no built-in automation, so if you need easier access or want to set automated retention policies, a third-party tool will be a better fit.
To archive a large custom object, start by exporting the data using Data Export or SOQL queries, so you have a clean backup before you archive any data. For very large volumes (millions of rows), use a dedicated third-party backup solution like Gearset to handle bulk jobs reliably. Gearset also makes it easy to confirm the backup completed successfully and surface any errors before you delete anything.
Once you’ve completed this process, free up space in your production org by deleting the original records after confirming the archive is safely stored and accessible.
How to implement a data retention policy in Gearset
If you want more space and more control over your data retention, Gearset provides automated retention rules, archiving, and backup options. This helps you ensure compliance without manual oversight. Gearset also lets you store older records outside of Salesforce, automate deletions, and ensure long-term data availability.
Archiving in Gearset
Gearset’s Salesforce archiving solution lets you set a data retention policy to automatically manage how long archived records are stored for before they’re permanently deleted. This helps free up storage in Salesforce, improving org performance while keeping historical data accessible for compliance, reporting, or future reference. And, as your archives aren’t stored on Salesforce’s servers, you’ll still have access even if Salesforce experiences an outage.
Here’s how to get started with an archive in Gearset:
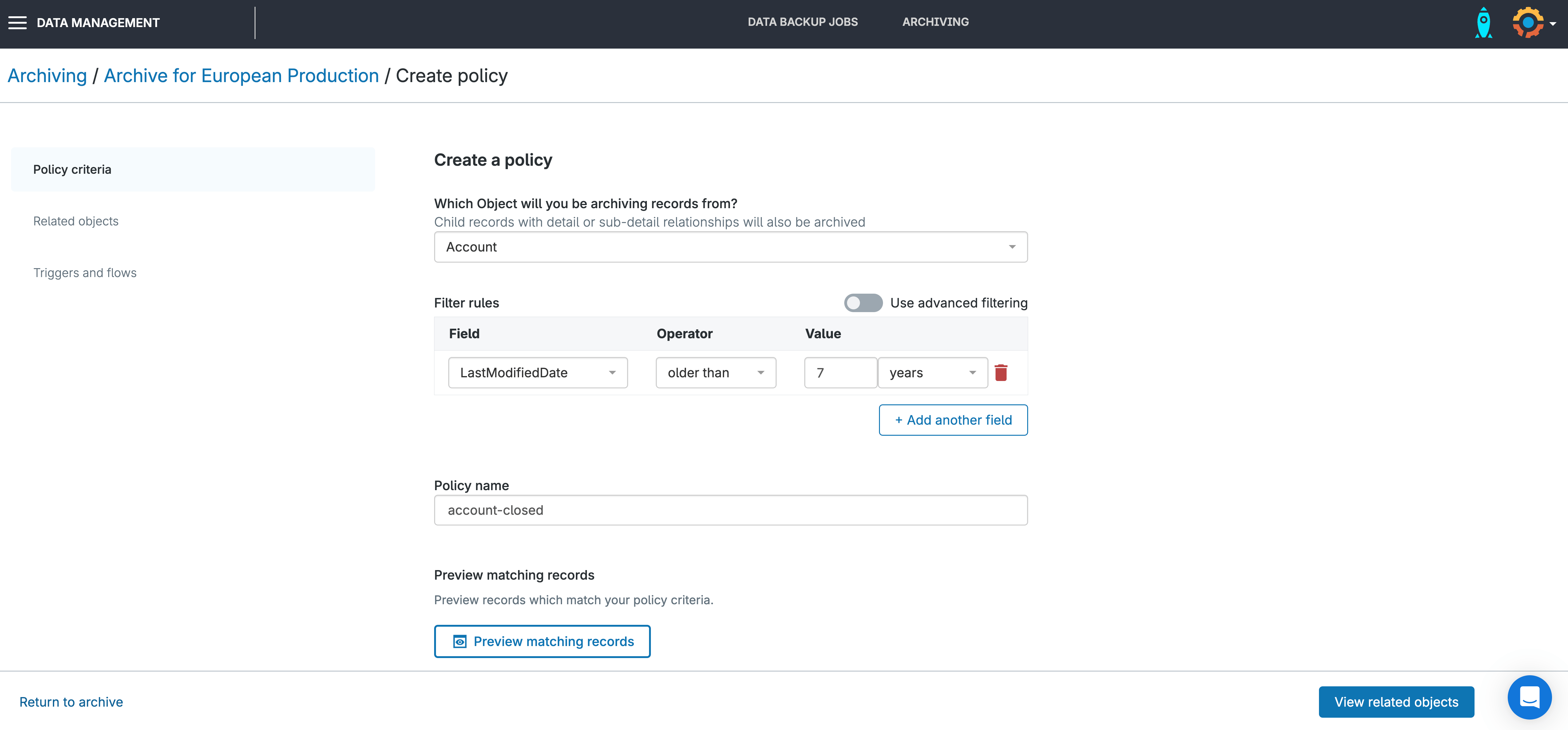
1. Create or edit an archiving policy: In Gearset, go to the Archiving tab and select an existing archive job or create a new one.
2. Set your retention rule: In the archiving policy settings, you’ll see the Policy criteria section. Choose how long Gearset should keep archived records before deleting them. By default, it’s set to 99 years, but you can adjust this to match your specific data retention and compliance needs.
3. Assign permissions to your team: Set strict permissions so you only give access to the people who need it. You can assign granular permissions ranging from simply viewing the archive to being able to delete or restore.
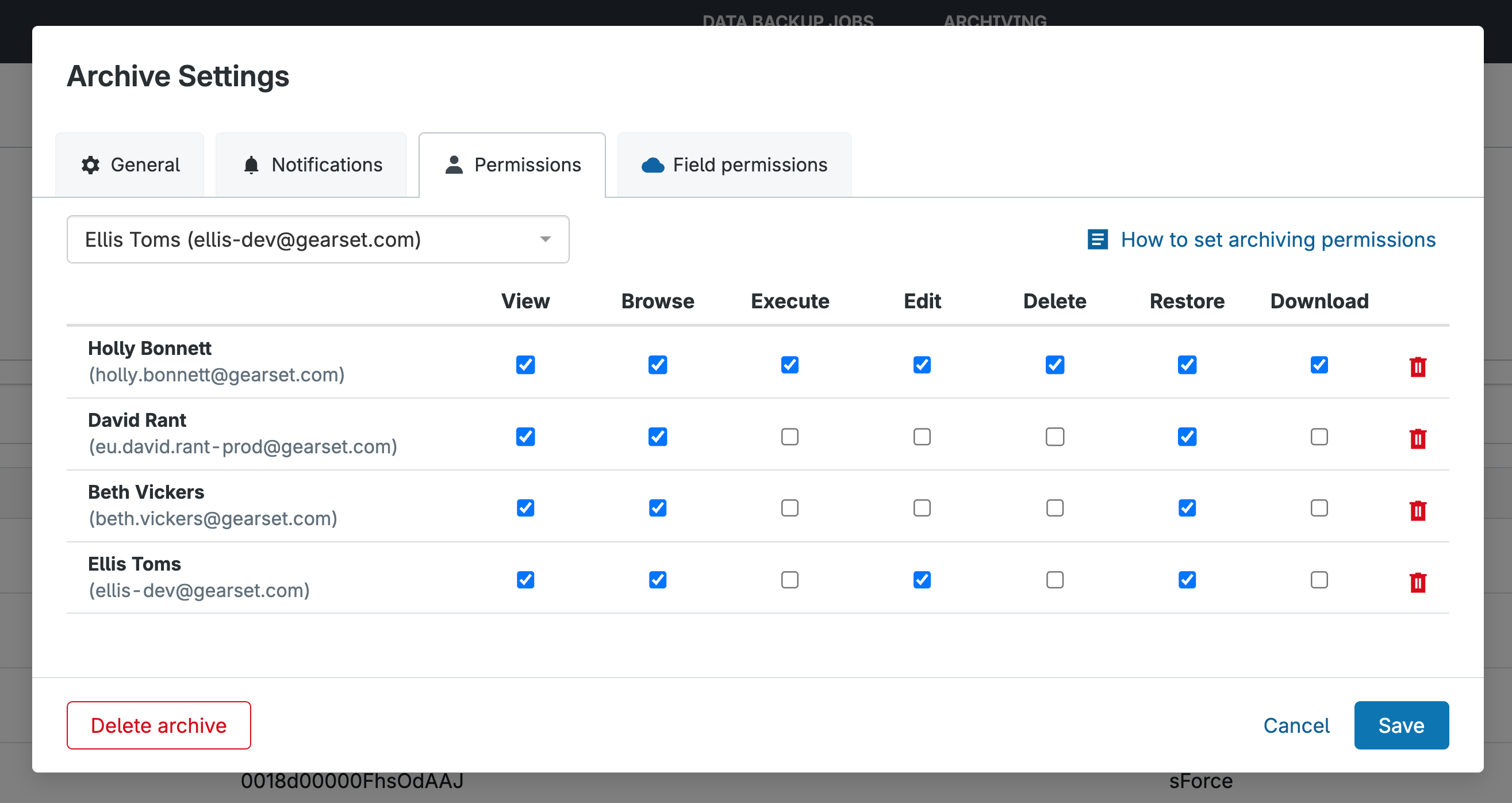
Retention rules are implemented per policy, so you can apply different retention periods to different types of data within the same archiving job. This gives you the flexibility to keep certain records for longer periods while ensuring others are removed when they’re no longer needed. As Gearset stores archives off-platform with unlimited storage, you won’t be forced to buy more Salesforce storage as your data grows.
Backup in Gearset
Data retention policies don’t just extend to archived data; they’re also crucial for your backups. Of course you need to keep backups long enough to be able to restore data, should anything be lost or corrupted. But you shouldn’t keep backup data forever. Decades-old data is unlikely to be relevant and needed for restoration — it’s simply a security and compliance liability.
Gearset’s backups give you scheduled, restorable snapshots of your org, capturing both Salesforce data and metadata. When you configure a backup job in Gearset, you define the retention policy and Gearset automatically deletes backup runs older than your specified timeframe. Gearset suggests a 7-year retention period by default as this matches the most common requirements for keeping financial records and audit trails, so you stay compliant without having to track it yourself.
Gain full visibility on data usage in your org
To manage data retention effectively, you need visibility. Understanding how your data is growing and changing over time is essential for preventing issues before they impact your org. This concept of monitoring changes and trends in your system is often referred to as observability, and it’s crucial for taking control of your data.
If you just want to know how much storage your organization is using right now, you can check the Storage Usage page in Salesforce. Head to Setup > Storage Usage to see a breakdown of your organization’s data and file storage, including usage by each standard and custom object.
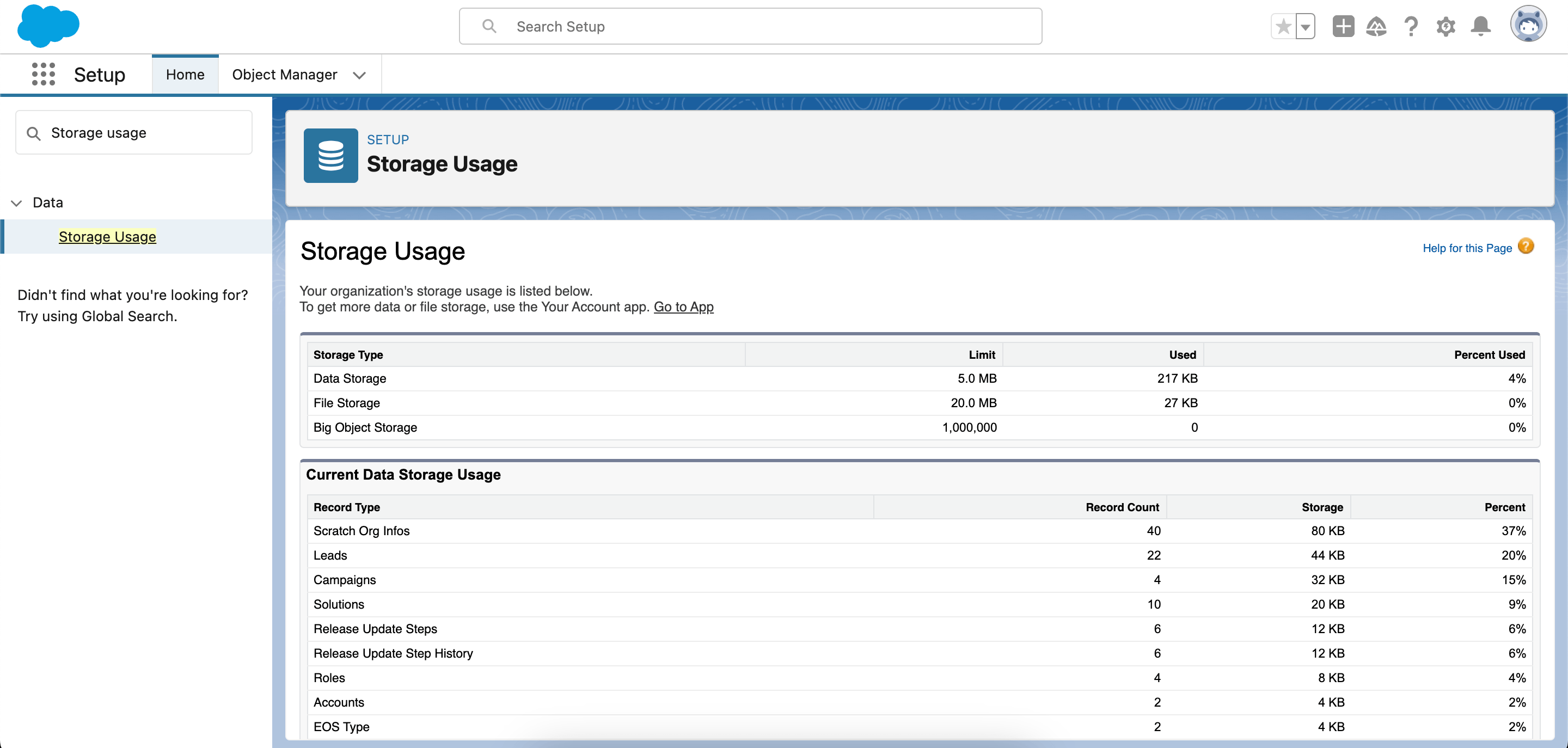
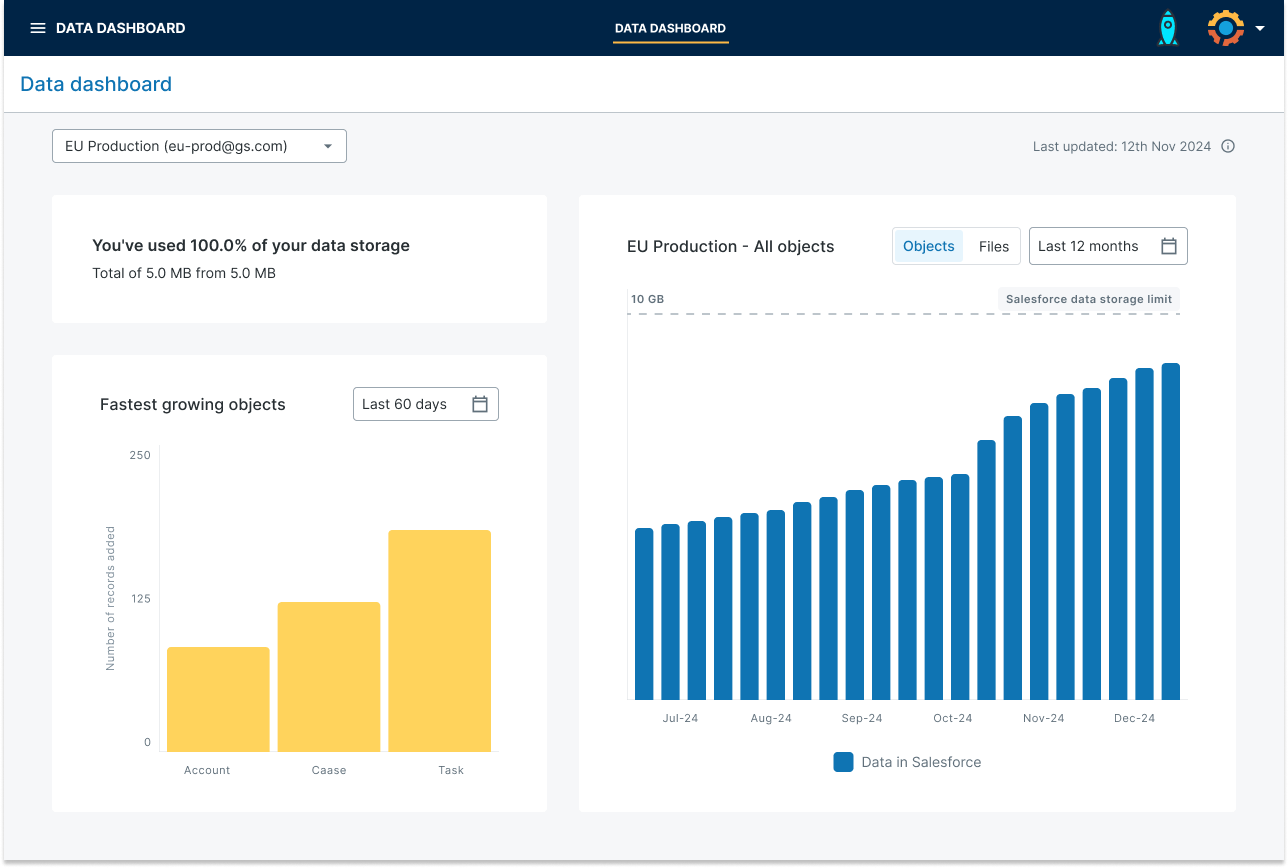
Go beyond a static view of storage with Gearset’s data dashboard. Available to backup customers, the data dashboard helps track storage trends, identify fast-growing objects, and catch unexpected data spikes.
Instead of just seeing a snapshot of your current storage usage, you get a clear view of how your data has changed, so you can predict when you might run out of space and take action before it happens. By building observability into data retention, teams can store what’s needed, archive or delete the rest with confidence, and keep their Salesforce environment lean and scalable.
Get control of your data
Backups and archives are the foundation of securing your Salesforce data, but if you can’t define and enforce retention policies, you’re vulnerable to compliance issues and security threats. Gearset empowers you to manage retention for both your backups and archives with confidence.
Retention isn’t just about storage limits — it’s about compliance, performance, and resilience. Manage backup and archiving in one place, keep your data lifecycle under control, and protect your Salesforce orgs with confidence.
If you need a hand getting started, speak to one of our DevOps experts for tailored advice on setting up a robust, secure backup solution — or start a free 30-day trial and try it yourself.